

This function is passed a LatLng and should return an instance of ILayer, in this case likely a Marker or CircleMarker. We can alter this by passing a pointToLayer function in a GeoJSON options object when creating the GeoJSON layer. By default simple markers are drawn for GeoJSON Points. Points are handled differently than polylines and polygons. Here's an example of a simple GeoJSON feature: var geojsonFeature = The reduce() method executes the specified reducer function on each. We can even use these properties to style our Leaflet vectors. Read this JavaScript tutorial and learn several methods used to find or calculate. The v-for directive requires a special syntax in the form of item in. Leaflet supports all of the GeoJSON types above, but Features and FeatureCollections work best as they allow you to describe features with a set of properties. We can use the v-for directive to render a list of items based on an array. Features in GeoJSON contain a Geometry object and additional properties, and a FeatureCollection contains a list of Features. GeoJSON supports the following geometry types: Point, LineString, Polygon, MultiPoint, MultiLineString, MultiPolygon, and Geometr圜ollection. The forEach () array method loops through any array, executing a provided function once for each array element in ascending index order. A GeoJSON object may represent a region of space (a Geometry), a spatially bounded entity (a Feature), or a list of Features (a FeatureCollection). In this example, you'll learn how to create and interact with map vectors created from GeoJSON objects.Īccording to GeoJSON Specification (RFC 7946): GeoJSON is a format for encoding a variety of geographic data structures.
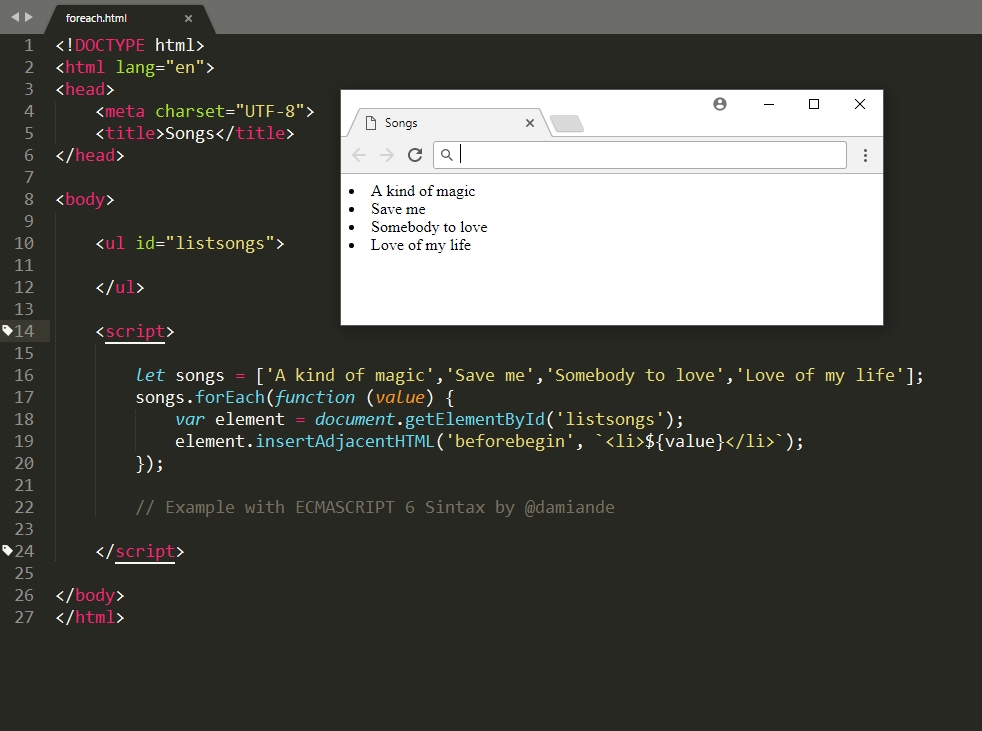
GeoJSON is a very popular data format among many GIS technologies and services - it's simple, lightweight, straightforward, and Leaflet is quite good at handling it.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
